igt-ai
IGT-AI AI gateway risk model
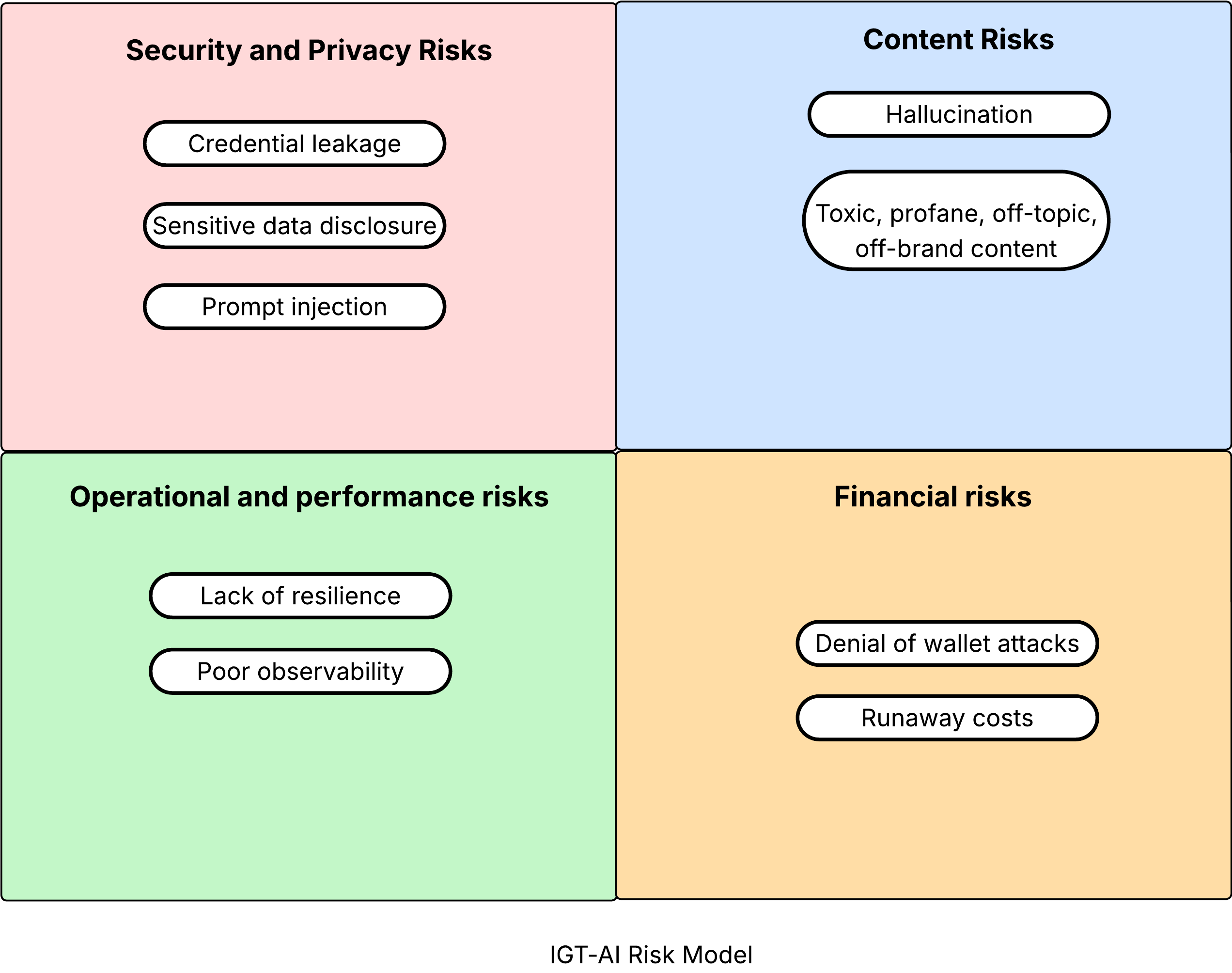
Consuming AI APIs exposes organizations to the following categories of risks.
- Security and privacy risks
- Content risk
- Operational and performance risks
- Financial risks
The different risks the IGT model covers within these categories are illustrated below.
In the sections below, for each risk category, I describe the specific risks and risk mitigation mechanisms at the AI gateway layer.
Security and privacy risks
Credential leakage
API keys and other credentials used to access AI APIs can be leaked through code repositories or logs, allowing unauthorized access to AI services.
Mitigation
Sensitive data disclosure
When sending data to AI APIs, sensitive information may be inadvertently included in requests to the LLM. Also, the LLM can also be tricked by an attacker into disclosing sensitive data, leading to potential data breaches or compliance violations. Example of sensitive data includes Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health information (PHI), financial data, or proprietary business information.
Mitigation
Prompt injection and jail breaking
Malicious actors can manipulate prompts sent to AI APIs to produce harmful or unintended outputs, leading to misinformation by the model, offensive content, or security vulnerabilities. See types of prompt injection.
Mitigation
Content risk
Hallucination
AI models may generate incorrect or fabricated information, which can mislead users or result in poor decision-making.
Mitigation
Toxic, profane, off-topic, and off-brand content
Attackers can send queries that are irrelevant to the business or out-of scope of the generative AI application. A model can produce outputs that are biased, offensive, or harmful, damaging the organization’s reputation and user trust. This includes vulgar, profane, or offensive language, hate speech, gratuitous violence, bullying, sexually explicit content, or any content that’s inconsistent with the brand’s voice and values.
Mitigation
Operational and performance risks
Lack of resilience
An inference service may become unavailable due to high demand, outages, or other issues, impacting application functionality. AI APIs can introduce latency into applications, especially if the API provider experiences high demand or outages, impacting user experience. Delays between user input and model input can lead to user frustration and reduced engagement.
Mitigation
Poor observability
Without proper logging, monitoring, and tracing of AI API calls, it can be challenging to diagnose issues and understand usage patterns.
Mitigation
Financial risks
Denial of wallet attacks
Attackers can exploit AI APIs by sending a high volume of requests, leading to unexpected costs and potential service disruptions.
Mitigation
Runaway costs
Without proper monitoring and controls, normal usage of AI APIs can lead to significant and unexpected expenses. This risk is also referred to as unbound consumption.